蘭宜錚副教授研究團隊發表研究成果於 Bioresource Technology
連結網址:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36252759/
Abstract
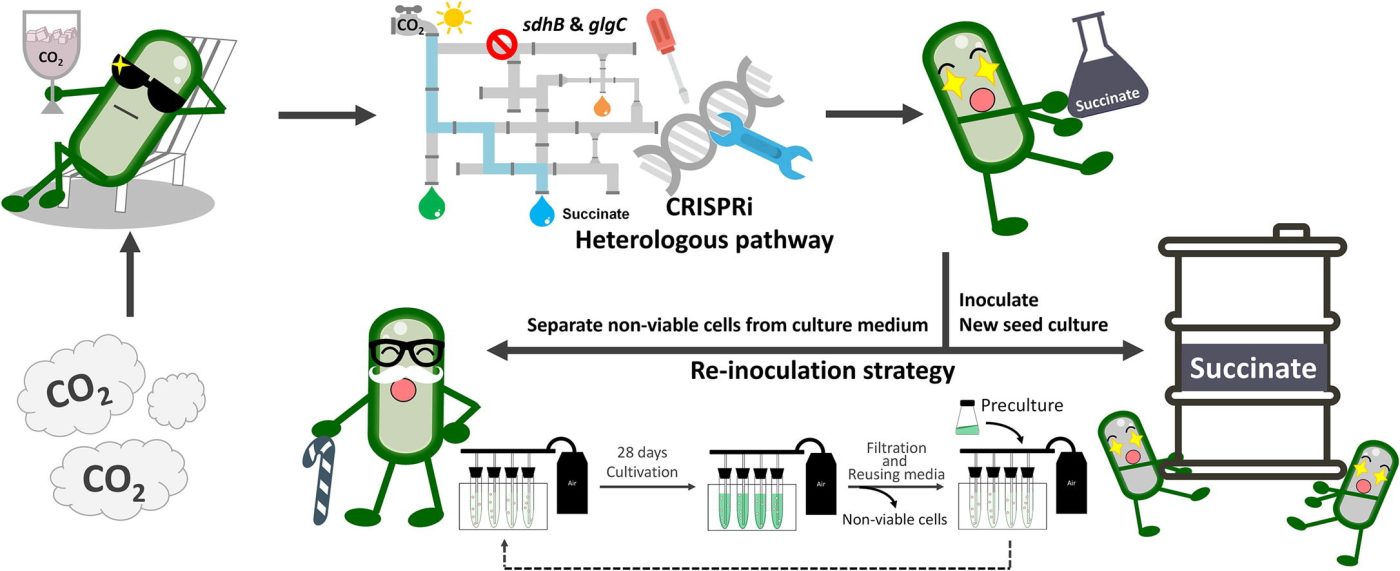
Engineering photoautotrophic microorganisms to directly convert carbon dioxide into platform chemicals is an attractive approach for chemical sustainability and carbon mitigation. Here, an engineered cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 was developed to produce succinic acid directly from ambient carbon dioxide. Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase and glycogen synthase by CRIPSR interference increased carbon flux towards succinic acid. Dual inhibition of these two genes led to an 82% increase in titer. The resulting strain produced 4.8 g/L of succinic acid in a 28-days cultivation. However, cells after the 28-days cultivation became non-viable and cannot continue production. This issue was addressed by re-inoculation with fresh cells into the production medium. This strategy enabled continuous succinic acid accumulation, reaching a final titer of 8.9 g/L. This study provides a sustainable route to succinic acid directly from carbon dioxide and a potential method to overcome the low titer limitation of cyanobacterial-based bioproduction for practical applications.